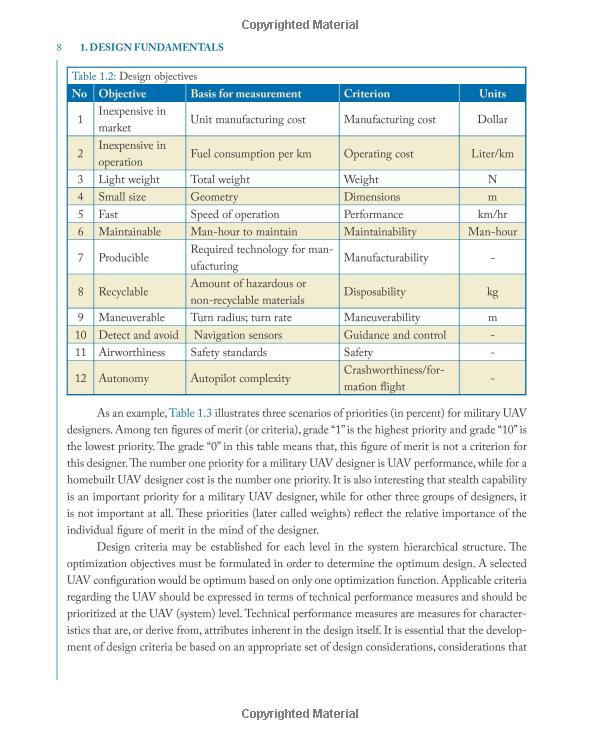
Title: Fundamental Knowledge of Chair Mat Engineering Apprenticeship
As an apprentice in chair mat engineering, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the fundamental principles and concepts that underlie this field. This includes knowledge of materials science, manufacturing processes, and design principles. One of the key areas of focus for an apprentice in chair mat engineering is the selection and use of appropriate materials for production. This involves analyzing factors such as cost, durability, and performance, and choosing materials that meet the specific needs of a given application. Another important aspect of chair mat engineering apprenticeship is learning about design principles such as ergonomics, safety, and user experience. This involves working closely with clients and end-users to understand their needs and preferences, and developing innovative solutions that meet these needs while also ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and standards. Overall, a successful apprenticeship in chair mat engineering requires a strong foundation in technical knowledge and practical skills, as well as a commitment to continuous learning and improvement. By staying up-to-date with the latest trends and developments in the industry, apprentices can position themselves for long-term success in this dynamic and exciting field.
Introduction to Chair Mat Engineering Apprenticeship
Chair mats, also known as floor mats or entrance mats, are an essential component of any indoor space. They provide protection for floors, reduce noise, and enhance the overall appearance of a room. However, behind the elegant design and functional features of these mats lies a complex process of manufacturing that involves various engineering disciplines. This article aims to introduce the fundamental knowledge of chair mat engineering apprenticeship, covering topics such as material selection, design principles, manufacturing processes, and quality control.
1. Material Selection and Properties
The choice of material is crucial in determining the characteristics of a chair mat, including durability, thickness, colorfastness, and anti-staining properties. Common materials used in chair mat production include PVC (polyvinyl chloride), rubber, polypropylene, and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE). Each material has its advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, resistance to wear and tear, and environmental impact. For example, PVC mats are generally less expensive but may not be as durable as TPE mats.
2. Design Principles
A successful chair mat should provide adequate support for people's feet while minimizing friction and slippage on hard or uneven surfaces. Designers must consider factors such as shape, size, texture, and pattern when creating chair mats. The ideal shape should conform to the shape of the user's feet, with a curved surface at the front and a flat surface at the back. The size should be appropriate for the room and the type of flooring it covers. The texture can vary from smooth to rough, depending on personal preferences and foot anatomy. Finally, the pattern can add visual interest and branding opportunities for companies.
3. Manufacturing Processes

There are several methods for producing chair mats, including injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, and rotational molding. Injection molding typically involves melting plastic resin and injecting it into a mold cavity to create a solid product. Extrusion molding involves stretching a raw material through a die to produce a linear profile. Blow molding involves inflating a hollow tube with air to form a spherical or cylindrical shape. Rotational molding involves rotating a mold around a central axis to create a continuous loop or tubular product. Each method has its advantages and limitations in terms of complexity, cost, and yield rate.
4. Quality Control
Quality control is critical in ensuring that chair mats meet customer expectations and industry standards. Inspection procedures may include visual examination, measuring dimensions using specialized tools, testing for durability and resistance to tears or stains, and conducting performance tests such as weight capacity or slip resistance. In addition to internal inspections by employees or third-party auditors, customers can also provide feedback through surveys or social media channels to help improve the quality of future products.
Conclusion: The Journey of a Chair Mat Engineer

In conclusion, learning about the fundamental knowledge of chair mat engineering apprenticeship requires understanding various aspects of material selection, design principles, manufacturing processes, and quality control. As someone embarks on this career path, they will need to develop technical skills in areas such as mathematics, physics, chemistry, and engineering mechanics. They will also need to cultivate interpersonal skills such as communication, teamwork, problem-solving, and leadership to work effectively with colleagues and customers from diverse backgrounds. By combining theoretical knowledge with practical experience and innovation, they can contribute to the development of high-quality chair mats that enhance comfort, safety, and aesthetics in our daily lives.
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Title: Unveiling the Elegance of Womens Ties: An In-Depth Exploration
The rise of the Feather-Filled Jacket
Title: Mastering the Art of Tying a Tie: A Step-by-Step Guide with Video Tutorials
Title: The Stylish and Famous Polo Ties from the Worlds Top Brands



